turn to top page
Chironomids larvae
search & classificationi
introduction
This homepage is gathered up the knowledge that I got so far for a person to start the study of the chironomids from now on.
I tried to serch and classify them to the stage of genus.
In the study of the chironomids , it is almost impossible to identify
the species with the form of the larva.
Because a quite different imago comes out from the larvae which seems the
same kind of larvae.
The chironomids which I used for this study are mainly gathered in fresh
water area in Japan.
このホームページの内容は、新しい情報をもとに今後変更していくことを含んで参考にしていただきたい。なお本ページに対するご意見、ご指摘があれば次のメールアドレスにお寄せください。
reichou@cty-net.ne.jp
北川禮澄
1 Where do the Chironomids larvae inhabit?
The most of the larvae of the chironomids inhabit in rivers and the wetlands
of the fresh water, but few chironomids inhabit in wet dead leaves ,soil
and the seawater besides.
I intended to take up only the chironomids which inhabit in the fresh water
in this homepage.
In rivers and the wetlands, the chironomids larvae live in the alge grown
surface on the rock and pebble. As for many chironomids living there , they don't make
their nests. But few chironomids make the nest fixed on the rock and the
nest which they can carry with them. In addition there are chironomids
inhabiting in the grit and mud of the bottom of the river and lake . Rather
there are more a kind and populations of chironomids living here than the
former.
There are chironomids which stick to the stem and the root of the aquatic
plant else.
The chironomid larvae live in the cool and clear rivers, in the torrent of the steep slope of the water fall, in the river of the spring ing out of the hot spring more than water temprature 40℃. and in messy area without almost dissolved oxygen.
In other words, it is their carasteristic that to be able to inhabit any
kind of emvironmental area of the water. The chironomids of the kind that
fitted each environment inhabit there . I tried the collection of the larva
more then 10,000 times till now.,but there was few that there was nothing
.
We are able to think that chironomid larvae inhabit any kind of place of
the fresh water area.
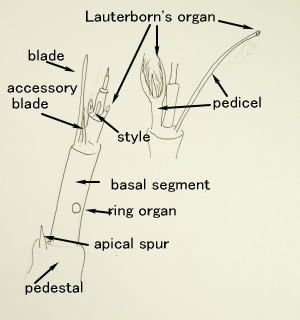
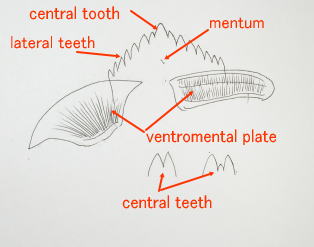
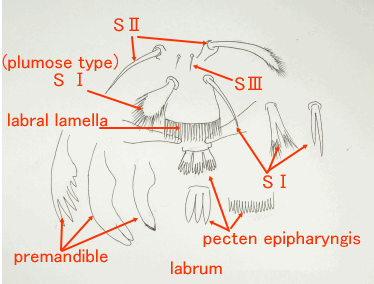
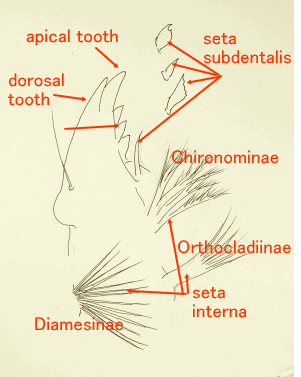
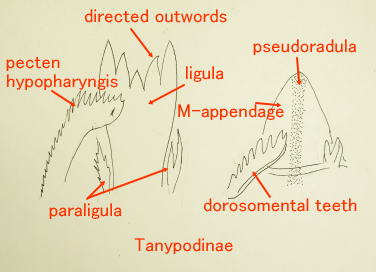
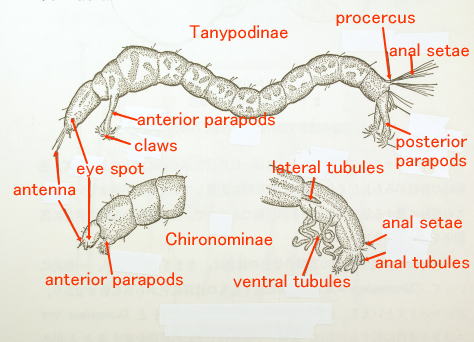
2 The names of the necessary parts for a classification ・How to research
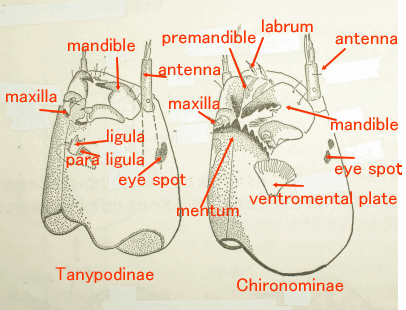 |
幼虫の分類に必要な部位と観察の方法
1:幼虫の生きている間に色を記録しておくことが必要である。死後は変色し、
特にアルコールで固定した場合は退色してしまう。
2:スライドグラス上にガムクロラールを滴下し、体から切り離した頭部を背面を
上にして置き、カバーグラスをかけて軽く指先で押し付けて、頭殻の形態を
スケッチとともに記録する。
3:カバーグラスを静かにはずし、頭部の腹面を上にする。ガムクロラールを少量
加え、カバーグラスをかけて、ガラスがずれないように、指先でかなり強く圧する。
4:尾端部は第10体節あたりから切り離し、スライドグラス上に滴下したガムクロ
ラールに載せ、封入する。この際指先で圧することはしない。圧すれば肛門鰓
や後擬脚は大きく変形する。
必要に応じて、尾剛毛は台の付け根から切りはずし、別に封入する。
サンプルが多数ある場合には背面、側面の標本を作る。
5:前擬脚は基部から切り離し、別に封入して、強く圧する。
6:体節の部分は背面を上にして封入する。
・1枚のスライドグラス上に上記2〜6のサンプルを並べるので、カバーグラスは
予め1/4の大きさに切断しておく。
・いずれの操作においてもサンプルの間に気泡が残らないようにしなければならない
{ガムクロラールの作り方}
グリセリン 3mg、 抱水クロラール 30g、 アラビアゴム 8g、 氷酢酸 1ml、
水 10ml
以上の薬品を混ぜ合わせ、弱く加熱しながら溶かす。 アラビアゴムが完全に溶け
ない時にはガラスウールで濾過する。
|
|
3 The references about the classification of the Chironomid larvae
図説日本のユスリカ 日本ユスリカ研究会編 , 文一総合出版, 2010
ユスリカの世界 近藤繁生他, 培風館, 2001
日本産水生昆虫検索図説 ユスリカ科 橋本碩 、川合禎次(編) 東海大学出版会編 1985
水生昆虫学 津田松苗 北隆館 1962
ユスリカ類概説 (1,2,3) 森谷清樹, 用水と排水, 1983
川と湖の博物館 北川禮澄, 山海堂, 1994
指標生物シリーズ 1 ユスリカ 北川禮澄, 山海堂, 1986
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(1) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 1999
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(2) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 2000
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(3) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 2001
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(4) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 2002
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(5) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 2003
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(6) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 2004
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(7) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 2005
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(8) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 2006
ユスリカの幼虫の分類(9) 北川禮澄, 淡水生物, 2007
Chironomidae of the Holarctic region , Keys and diagnoses Part 1 , Larvae . W. TORGNY, Entomologica Scandinavica
, 1983
The biology and Identification of the Chironomid , Bryce and Horbart , Entmologist’s Gazette,vol1, 1972
Aquatic Insect of California ROBERT L. USINGER, UNIVERSITY OFCALIFORNIA PRESS , 1956
Aquqtic Diptera O.A.Johannsen Cornell University, 1973
4 Search and Classification
Chironomids which I recorded so far are 6 subfamilies, 120 genera and about
800species in Japan. In this home page , I took up the chironomids gathered in the country
and 3 genera ( Goeldichironomus, Nimbocella, Odontomesa) gathered in abroad.
to Search and classification
1 Tanypodinae
2 Chironominae
3 Orthocladiinae
4 Diamesinae
5 Prodiamesinae
6 Podonominae
return to top of this page